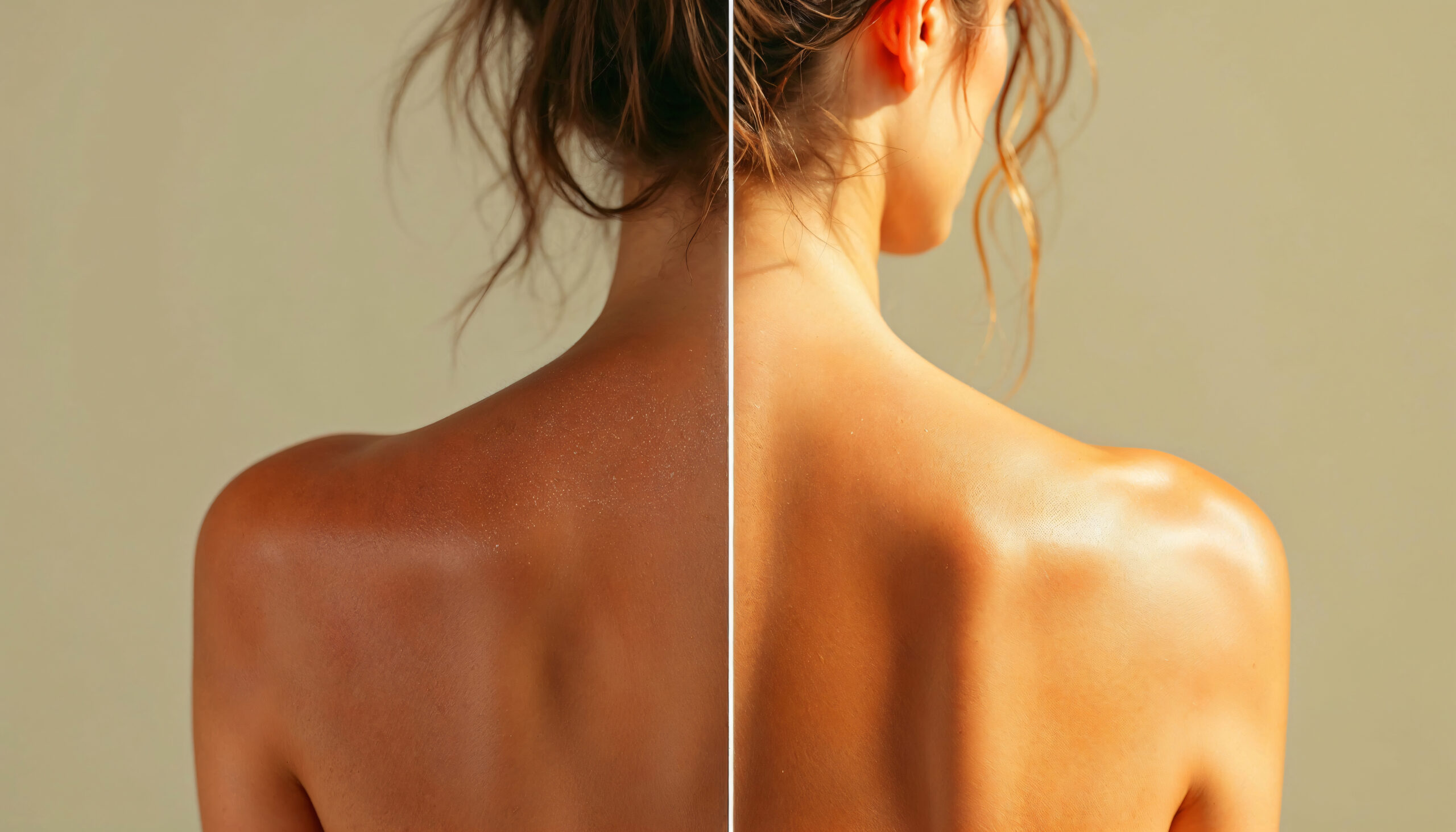
Sunscreen is not just an essential ally for avoiding sunburn on beach days — it’s a year-round necessity for protecting your skin’s health. Applying a sunscreen with an effective sun protection factor (SPF) helps shield the skin from the harmful effects of ultraviolet (UV) rays, particularly UVA and UVB radiation.
Why You Should Use Sunscreen Every Day
Daily use of sunscreen significantly reduces the risk of:
- Premature skin aging: UVA rays penetrate deeply into the skin, accelerating the formation of wrinkles, sun spots, and loss of elasticity.
- Sunburn and immediate damage: UVB rays affect the skin’s surface layers, causing redness, irritation, and in severe cases, burns.
- Skin cancer: Prolonged, unprotected exposure increases the likelihood of developing actinic keratosis, carcinomas, and melanomas.

How Sunscreen Works
Sunscreen creates a protective barrier that limits the absorption of UV rays by the skin. There are two main types of filters used in sunscreen formulas:
- Physical (mineral) filters: Ingredients like zinc oxide and titanium dioxide reflect and scatter UV rays, acting as a shield.
- Chemical filters: These absorb UV radiation and convert it into harmless heat, preventing cellular damage.
The sun protection factor (SPF) indicates how much longer you can stay in the sun without burning compared to unprotected skin. For instance, an SPF 30 sunscreen allows you to stay out 30 times longer before burning. However, no sunscreen provides 100% protection.
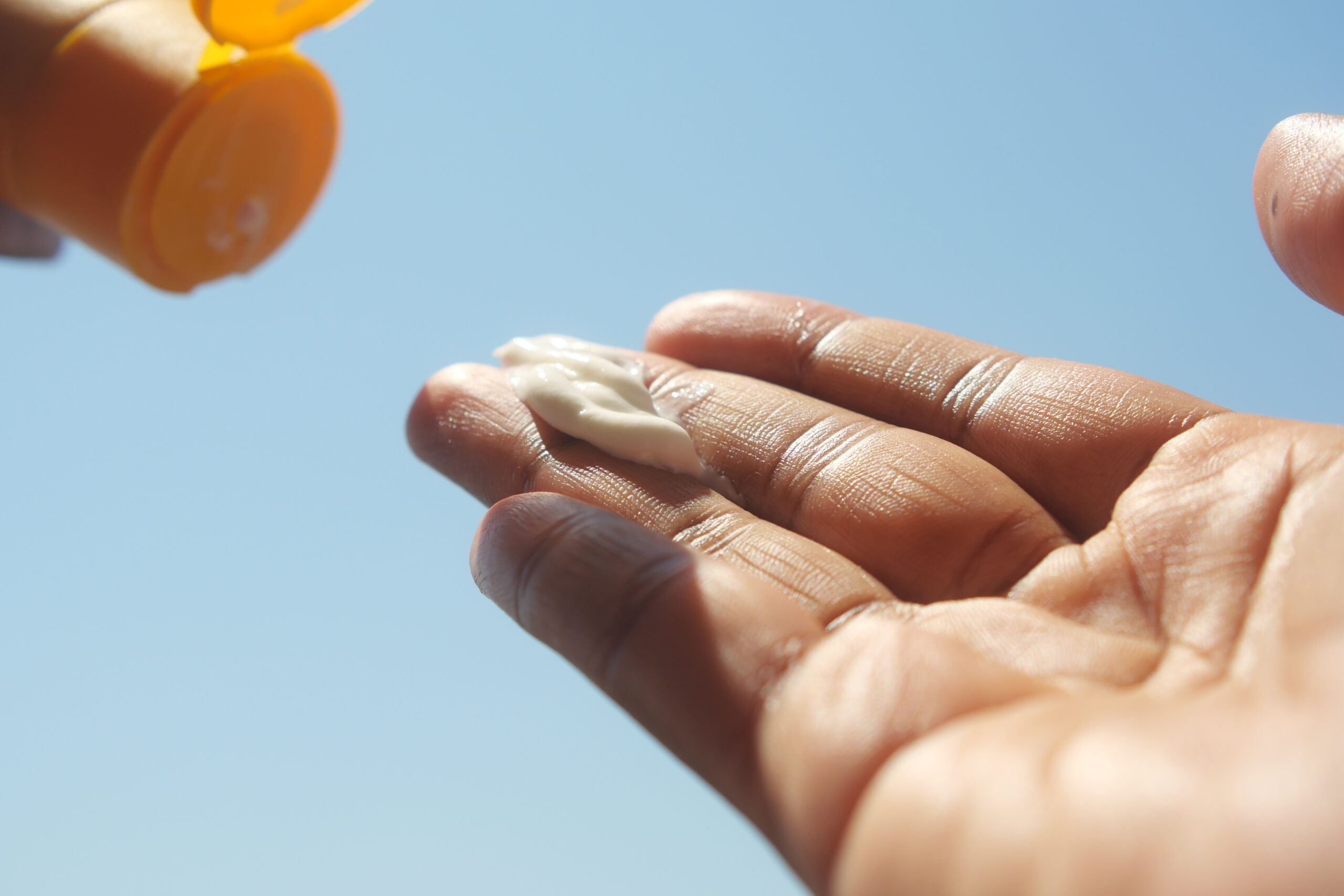

How to Apply Sunscreen Properly
To ensure maximum protection:
- Apply sunscreen 20-30 minutes before sun exposure.
- Reapply every two hours, and always after swimming, heavy sweating, or towel-drying.
- Choose an SPF suitable for your skin type and conditions — for example, SPF 50+ for children or high-altitude environments.
- Don’t forget often-neglected areas: ears, the backs of hands, feet, and the scalp in those with thinning hair.
Why Reapplying Every Two Hours Is Essential
One of the most common mistakes is applying sunscreen once in the morning and assuming you’re covered for the day. In reality, protection diminishes over time due to several factors:
- Sweating: Sweat dilutes and washes away sunscreen.
- Swimming: Even water-resistant sunscreens lose their effectiveness after time in the water.
- Friction: Toweling off, changing clothes, or sitting down can rub sunscreen off the skin.
- Filter breakdown: UV rays and oxygen gradually degrade the active ingredients in sunscreens.
Dermatologists recommend: Always reapply sunscreen every two hours of continuous exposure, and immediately after swimming or sweating — even if less time has passed.
Sunscreen: A Daily Habit
Sunscreen isn’t just for beach days. UVA rays penetrate clouds and glass, meaning your skin is at risk even in the city or while driving. Applying a sunscreen with UV filters every morning is a simple habit that helps prevent premature aging and more serious damage, keeping your skin healthy and radiant over time.